1. Latest articles
The latest scientific publications of our department with a short summary.
A high-quality corpus of Dutch ICU medical notes was created to help computers detect medication side effects, especially those impacting the kidneys. Two medical experts analyzed anonymized notes from 102 adult ICU patients suspected of having drug-related kidney issues. They labeled medications, medical problems, and their relationships using standardized, double-checked guidelines. Over 16,000 labels were added in total, including 614 for drug-related side effects. The resulting dataset will be used to train computer systems to identify side effects in Dutch electronic medical records automatically.
Rachel O'Sullivan-Murphy, et el DOI: 10.1007/s10579-025-09832-5
This study identified a chronic kidney disease (CKD) cohort from Amsterdam UMC using electronic health records based on six logical rules.
Pooling these six logical rules resulted in identifying 17 805 hospitalized CKD patients (16.4%). The proportions identified by each logical rule varied from 2.1% to 8.4%. Our findings highlight the need to formalize the CKD clinical definition into a computer-interpretable one, to avoid inconsistencies in EHR implementation across studies.
Daniel Fernandez Llaneza, et el DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaf073
This study created two AI models to help detect lung cancer early by analyzing doctors’ notes and other health information.
One model was based on these notes alone and the other combined the notes with other health data. Both models worked well in spotting patients at high risk for lung cancer. The model that included both the notes and other data was slightly more accurate.
Iacopo Vagliano, et el DOI: 10.3390/cancers17071151
This study identified barriers to implementing the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles in child and adolescent mental health research.
A total of 45 barriers were identified, including those related to organizational policies and software. Key recommendations include adding a FAIR data steward to the research team, providing accessible guides, and ensuring sustainable funding to overcome these barriers, ultimately enhancing data reusability.
Rowdy de Groot, et el DOI: 10.2196/59113
Machine learning models often struggle to generalize to data distributions that differ from their training dataset, known as "out-of-distribution" (OOD) data. It is important to detect OOD because prediction on such data can be unreliable.
While OOD detection methods have been explored in various fields, their effectiveness for medical data remains unclear. This study aims to evaluate and compare different OOD detection methods in the context of medical tabular data.
The visual summary and interview with Giovanni Cina explains OOD.
Mohammad Azizmalayeri, et al DOI:10.1016/j,ijmedinf.2024.105762
2. PhD theses
The latest PhD theses of our department.
3. Research in the spotlight
Researchers of our department in the spotlight! With a visual summary and a short interview. Curious? Click on the figures to find out more.
Digital tools in cancer screening
Interview with Corine Oldhoff-Nuijsink, researcher on Human Factors Engineering.
Federated learning in the healthcare setting
Interview with Sebastian van der Voort, researcher on Quality of care (IT systems), Methods in Medical Informatics and Reusable Health Data
Detecting unreliable predictions of ML models
Interview with Giovanni Cinà, researcher on Methods in Medical Informatics
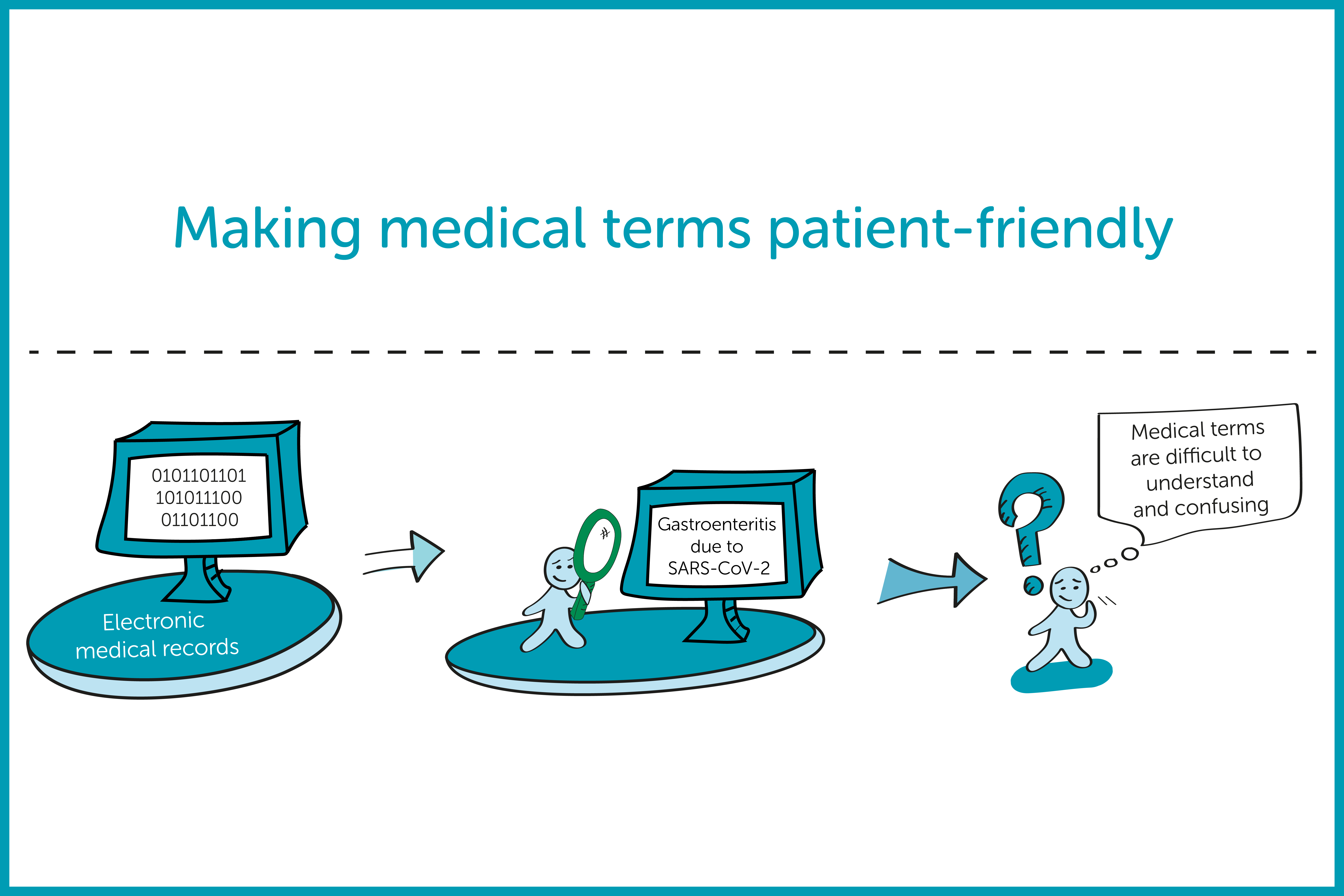
Making medical terms patient-friendly
Interview with Hugo van Mens, researcher on Reusable Health Data
4. Broodje MedInfo (Sandwich MedInfo)
🍞 Are you interested in or working on a data-driven (research) project in healthcare? And would you like to know more about best practices for your project? Then broodje MedInfo is for you!
This online event includes research results, tips for your own data project and time for questions. Below, you can find the recordings of previous editions on FAIR, LLMs, Audit & Feedback and Usability.
Usable computer systems
In this edition, Linda Dusseljee-Peute spoke about usable computer systems (e.g. apps, decision support systems, and electronic health records), human-computer interaction, design and the currently available evidence.
Quality registrations and Audit & Feedback
Nicolette de Keizer and Ferishta Bakhshi-Raiez presented, in Dutch, results of continuous improvement using a quality registration in specialist medical care and the implications of a new Dutch law.
LLMs
Iacer Coimbra Alves Cavalcanti Calixto presented, in English, the opportunities and challenges of Large Language Models in healthcare. Including patient privacy, model interpretability, and reducing administrative burden.
Ronald Cornet presented in the first edition, in Dutch, the importance of the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) Principles and how you can apply them in projects. Look here for the tips from the Q&A.
5. Podcast Health Informatics (in Dutch)

6. Technical reports
Check here for all our technical reports!